Anterior hip precautions are essential for safe recovery after hip surgery, focusing on preventing dislocation and promoting healing. Physical therapy begins immediately, emphasizing proper movement and patient education to ensure optimal outcomes.
What Are Anterior Hip Precautions?
Anterior hip precautions are specific guidelines designed to protect the hip joint after surgery, particularly following an anterior total hip replacement. These precautions aim to minimize the risk of dislocation and promote proper healing. Patients are advised to avoid certain movements, such as bending past 90 degrees, excessive leg separation, and turning without using a pillow between the legs. Weight-bearing status and the use of assistive devices, like crutches or walkers, are also critical components. These measures ensure the hip joint remains stable during the recovery process. By adhering to these precautions, patients can reduce complications and achieve a successful outcome. Proper adherence to these guidelines is essential for safeguarding the surgical site and ensuring optimal recovery.

Why Are Anterior Hip Precautions Important in Physical Therapy?
Anterior hip precautions are crucial in physical therapy to ensure a safe and effective recovery after hip surgery. These guidelines help prevent complications, such as dislocation or improper healing, by limiting risky movements. By adhering to precautions, patients protect the surgical site and allow the hip joint to heal properly. Proper alignment and stability are maintained, reducing the risk of revision surgery. These precautions also guide patients in using assistive devices correctly and avoiding harmful positions, such as bending past 90 degrees or excessive leg separation. Following these measures minimizes discomfort, promotes tissue healing, and supports the return to normal activities. Ultimately, anterior hip precautions are essential for achieving optimal outcomes and ensuring long-term hip function and mobility.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Anterior Hip Precautions
Physical therapy plays a vital role in guiding patients through safe recovery, emphasizing adherence to anterior hip precautions to prevent dislocation and promote proper healing and mobility.
Goals of Physical Therapy After Anterior Hip Surgery
The primary goals of physical therapy after anterior hip surgery include restoring hip mobility, strengthening surrounding muscles, and improving balance and coordination. Therapy aims to minimize pain and inflammation, ensuring proper healing and preventing complications. Patients learn to use assistive devices like crutches or walkers to avoid excessive weight-bearing or harmful movements. Education on proper posture, sitting, and transferring techniques is crucial to maintain hip stability. The therapy also focuses on progressively increasing weight-bearing status as permitted by the physician. By adhering to these guidelines, patients can safely return to daily activities and achieve long-term functional recovery. The ultimate goal is to help patients regain independence and resume their normal lifestyle with minimal restrictions.
Key Components of a Physical Therapy Program
A comprehensive physical therapy program for anterior hip precautions typically includes therapeutic exercises, manual therapy techniques, and patient education. Therapeutic exercises focus on improving hip mobility, strength, and flexibility, while manual therapy may involve soft tissue mobilization or joint mobilizations to enhance movement. Patient education is critical, emphasizing proper posture, movement techniques, and activity modifications to protect the hip. Assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, are often incorporated to reduce strain during mobility. Pain management strategies, including ice or heat therapy, are also addressed. Regular progress monitoring ensures adjustments to the program as needed. The combination of these elements helps patients safely transition back to daily activities and supports long-term recovery. Each component is tailored to the patient’s specific needs and surgical guidelines to optimize outcomes and prevent complications.
The Role of the Physical Therapist in Patient Education
The physical therapist plays a vital role in patient education following anterior hip surgery. They provide personalized guidance on safe movement techniques, proper posture, and activity modifications to prevent complications. Therapists demonstrate exercises and precautions, ensuring patients understand how to protect their hip during daily activities. Education includes instructions on using assistive devices, managing weight-bearing status, and avoiding high-risk positions. Visual aids, such as diagrams or videos, are often used to reinforce instructions. The therapist also addresses patient concerns and answers questions to promote adherence to the recovery plan. Regular follow-ups allow the therapist to assess understanding and provide ongoing support. Effective education empowers patients to take an active role in their recovery, reducing the risk of setbacks and promoting a safe return to normal activities.

Understanding Anterior Hip Precautions for Patients
Anterior hip precautions are crucial for patients to avoid risky movements post-surgery, ensuring proper healing and preventing dislocation. Adhering to these guidelines is vital for a successful recovery.
Immediate Post-Surgery Precautions
Immediately after anterior hip surgery, patients must adhere to specific precautions to protect the hip joint and promote healing. These include avoiding movements that bend the hip past 90 degrees, such as deep sitting or bending forward. Patients should also avoid crossing the operated leg over the midline of the body or turning the leg inward. Using assistive devices like crutches or a walker is essential to minimize weight-bearing and reduce strain on the hip. Pain management and swelling control, often through elevation and ice, are critical during this phase. Patients are typically advised to follow a specific weight-bearing status, which may involve partial or full weight-bearing, depending on the surgeon’s instructions. Adhering to these precautions helps prevent complications, such as dislocation, and ensures proper healing of the hip joint during the initial recovery period. Compliance is vital to achieve the best outcomes and avoid setbacks.
Long-Term Activity Modifications
Long-term activity modifications are essential for maintaining hip health and preventing complications after anterior hip surgery. Patients are often advised to avoid high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, which can strain the hip joint. Instead, low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or brisk walking are recommended to promote mobility without excessive stress. Proper posture and body mechanics should be maintained during daily activities to reduce the risk of dislocation or wear and tear. Sitting for prolonged periods should be avoided, and cushions or pillows can be used to support the hip in a safe position. Additionally, patients are encouraged to modify repetitive movements that involve heavy lifting, bending, or twisting. These adjustments help ensure long-term stability and functionality of the hip joint, allowing patients to return to a fulfilling and active lifestyle while minimizing the risk of future issues.
Using Assistive Devices Correctly
Using assistive devices correctly is crucial for safe recovery after anterior hip surgery. Common devices include crutches, walkers, canes, and sliding boards. These tools help reduce stress on the hip joint and prevent dislocation. Patients should use crutches or walkers to avoid bearing weight on the affected hip, ensuring proper gait and balance. Canes can be used as strength improves but should be held on the opposite side of the affected hip. Sliding boards and reachers assist with transfers and reaching, minimizing the need for bending or twisting. Proper fitting and training on device use are essential to avoid complications. Patients should follow their physical therapist’s guidance to ensure safe and effective use, promoting independence while protecting the hip during healing. Correct use of assistive devices is key to achieving optimal recovery outcomes and preventing setbacks.
Importance of Patient Compliance
Patient compliance is essential for successful recovery after anterior hip surgery. Adhering to the prescribed physical therapy plan ensures proper healing and minimizes complications. Patients must follow activity restrictions, attend therapy sessions, and perform home exercises as directed. Compliance reduces the risk of dislocation, promotes strength, and restores function. It also accelerates recovery, allowing patients to return to daily activities sooner. Non-compliance can lead to prolonged recovery, increased pain, or the need for additional procedures; Clear communication between the patient and physical therapist is key to understanding the importance of compliance. Patients who actively participate in their care achieve better outcomes and regain independence faster. Compliance fosters a safe and effective recovery process, ensuring the best possible results from anterior hip precautions and physical therapy interventions.
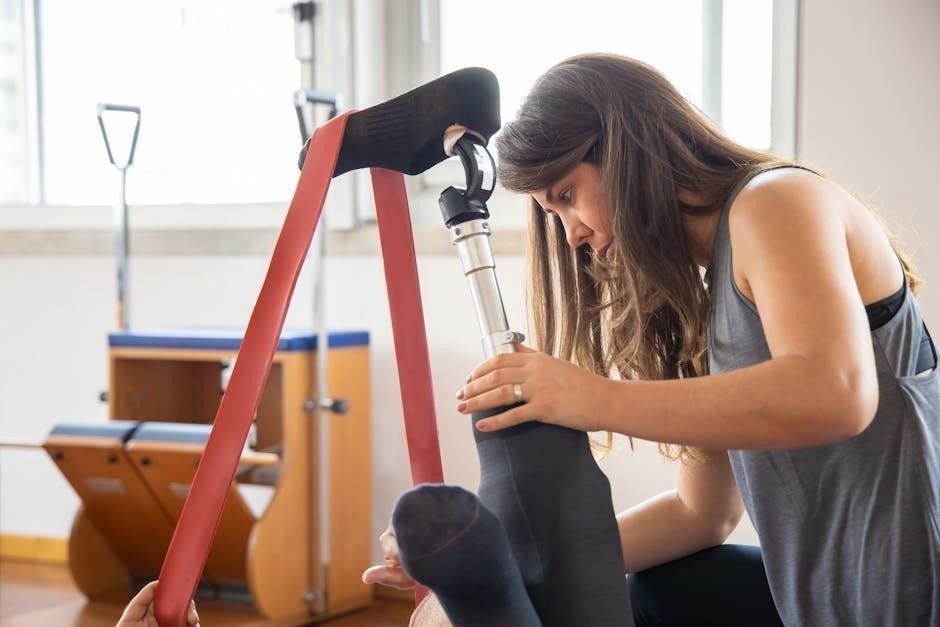

Exercises and Activities in Anterior Hip Recovery
Exercises and activities play a crucial role in anterior hip recovery, focusing on improving mobility, strength, and flexibility while avoiding harmful movements. A structured program ensures safe progression.

Early-Stage Exercises for Hip Mobility
In the early stages of recovery, gentle exercises are essential to restore hip mobility without compromising the surgical site. Heel slides, performed by slowly sliding the heel toward the buttocks, help improve flexion and reduce stiffness. Ankle pumps, which involve flexing and extending the foot, promote blood flow and prevent swelling. Ankle pumps, which involve flexing and extending the foot, promote blood flow and prevent swelling. Straight leg raises, lifting the leg without bending the knee, strengthen the hip muscles while minimizing stress on the joint. These exercises should be done within a pain-free range and progressively increased as tolerance allows. Breathing techniques and proper positioning, such as elevating the leg, are also emphasized to enhance comfort and effectiveness. A physical therapist will tailor these exercises to the patient’s specific needs, ensuring a safe and gradual return of hip mobility.
Strengthening Exercises for the Hip and Surrounding Muscles
Strengthening exercises are critical for restoring hip function and promoting long-term stability. Clamshell exercises, where the patient squeezes the legs together while lying on their side, target the gluteal muscles. Glute bridges, involving lifting the hips while lying on the back, enhance hip extension and core engagement. Side-lying leg lifts strengthen the hip abductors, crucial for maintaining proper gait and balance. Straight leg raises, performed in various positions, focus on isolating and strengthening the hip flexors and quadriceps. These exercises help improve joint stability, reduce muscle atrophy, and prevent compensatory movements. Progression involves adding resistance, such as elastic bands, or increasing repetitions and sets as strength improves. Proper form and alignment are emphasized to avoid strain on the surgical site. A tailored exercise program ensures the patient regains the strength needed for daily activities and mobility.
Activities to Avoid During Recovery
During recovery from anterior hip surgery, it is essential to avoid activities that could disrupt the healing process or compromise the surgical site. Patients should refrain from heavy lifting, bending, or twisting, as these movements can strain the hip joint. Sitting in low chairs, crossing legs, or placing the affected leg behind the body should also be avoided to prevent excessive hip flexion or external rotation. High-impact activities, such as running, jumping, or repetitive pivoting, are contraindicated until full strength and stability are restored. Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing without regular breaks can help reduce stiffness and promote circulation. Strict adherence to these restrictions ensures proper healing, minimizes the risk of complications, and supports a successful recovery. Patients should consult their physical therapist or surgeon for personalized guidelines on activity limitations.

Recovery Timeline and Expectations

Recovery from anterior hip surgery typically follows a structured timeline, with gradual progression through healing phases. Patients can expect to resume normal activities within 3-6 months post-surgery, depending on individual progress and adherence to therapy protocols.
Phase 1: Immediate Post-Surgery Recovery
The initial recovery phase, typically lasting 0-2 weeks post-surgery, focuses on pain management, swelling reduction, and basic mobility. Patients are advised to avoid weight-bearing on the affected hip and use assistive devices like crutches or walkers. Gentle exercises, such as ankle pumps and heel slides, are introduced to prevent stiffness and promote circulation. Wound care and adherence to hip precautions are emphasized to minimize dislocation risks. Patients are educated on proper positioning, such as avoiding flexion beyond 90 degrees or internal rotation. Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing progress and address any concerns. Pain and inflammation are managed through medication and ice therapy. This phase lays the foundation for a safe and effective recovery, ensuring the hip joint stabilizes before progressing to more active movements.
Phase 2: Progressive Strengthening and Mobility
Phase 2 typically begins 2-6 weeks post-surgery, focusing on gradually increasing strength and mobility while adhering to anterior hip precautions. Patients progress to weight-bearing exercises, such as partial weight-bearing walks, under the guidance of a physical therapist. Strengthening exercises target the hip flexors, abductors, and core muscles to restore functional stability. Gentle stretching is introduced to improve range of motion, avoiding movements that violate hip precautions. Assistive devices may still be used but with reduced reliance. Pain management continues, with a shift toward active recovery. Patient compliance with prescribed exercises and activity modifications is critical to prevent setbacks. This phase emphasizes rebuilding strength and confidence, preparing the patient for more dynamic movements in subsequent phases. Regular follow-ups with the physical therapist ensure proper progression and address any emerging concerns.
Phase 3: Return to Normal Activities
Phase 3 marks the transition back to normal activities, emphasizing the safe resumption of daily routines and hobbies. Patients gradually reintegrate into their pre-surgery lifestyle, guided by their physical therapist. This phase typically begins several months post-surgery, once strength, mobility, and stability are restored. Activities like driving, stair navigation, and light exercise are often reintroduced, with careful attention to anterior hip precautions to prevent overexertion. The physical therapist provides personalized advice to ensure patients avoid high-risk movements and activities that could jeopardize recovery. Emotional challenges, such as the temptation to rush back to normal activities, are addressed through patient education and support. This phase balances the desire for normalcy with the necessity of protecting the hip from improper stress, ensuring a smooth and sustainable return to daily life without compromising healing.
Special Considerations in Anterior Hip Recovery
Special considerations include weight-bearing status, pain management, and avoiding risky positions to ensure proper healing and prevent complications during recovery.
Weight-Bearing Status and Precautions
Weight-bearing status is a critical factor in anterior hip recovery, as it directly impacts healing and stability. Patients are often advised to follow specific weight-bearing precautions, such as toe-touch weight-bearing (TTWB) or non-weight-bearing (NWB), depending on the surgeon’s instructions. TWWB allows minimal pressure on the affected leg, while NWB requires avoiding any weight-bearing activity. Assistive devices like crutches or walkers are essential to adhere to these guidelines and prevent complications. Proper training on device usage is vital to ensure safety and compliance. Patients must avoid pivoting, bending, or twisting at the hip to minimize the risk of dislocation or implant instability. Regular follow-ups with the physical therapist are necessary to monitor progress and adjust weight-bearing status as healing advances. Adhering to these precautions ensures optimal recovery and prevents setbacks, allowing patients to gradually return to normal activities. Compliance with weight-bearing restrictions is paramount for achieving long-term success.
Management of Pain and Swelling
Effective management of pain and swelling is essential for a smooth recovery after anterior hip surgery. Patients are often advised to use ice therapy to reduce inflammation, with applications of 15–20 minutes several times a day. Elevation of the affected leg above heart level can also help minimize swelling. Gentle exercises, such as ankle pumps and heel slides, can improve circulation without overexertion. Pain management may include prescribed medications, but these should be used cautiously and as directed by healthcare providers. Additionally, modalities like electrical stimulation or ultrasound may be incorporated in physical therapy to alleviate discomfort. Monitoring pain levels is crucial, as persistent or increasing pain could indicate a complication. Patients should avoid activities that exacerbate pain and focus on balancing rest with controlled movements to support healing. Open communication with the healthcare team ensures personalized strategies for managing pain and swelling effectively throughout the recovery process.
Addressing Complications or Setbacks
Addressing complications or setbacks is critical to ensure a successful recovery after anterior hip surgery. Patients should monitor for signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or swelling around the surgical site, and report them immediately. Dislocation is a potential risk, particularly in the early stages, and may require immediate medical attention. Blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis, are also a concern and can be mitigated with prescribed medications or compression devices. If a setback occurs, the physical therapist may adjust the treatment plan to address the issue while promoting continued progress. Open communication between the patient and healthcare team is vital to identify and resolve complications promptly. Regular follow-ups and imaging studies may be necessary to assess the hip’s healing process and address any unexpected challenges. Early intervention often prevents minor issues from becoming significant problems, ensuring the recovery stays on track.
